Transactional 어노테이션에 대해 알아보자
스프링에서 간단히 @Transactional을 적는 것으로, 쉽게 트랜잭션을 구현할 수 있습니다. 어떻게 이 과정이 수행되는지 궁금했고 코드를 보면서 분석을 해보았습니다.
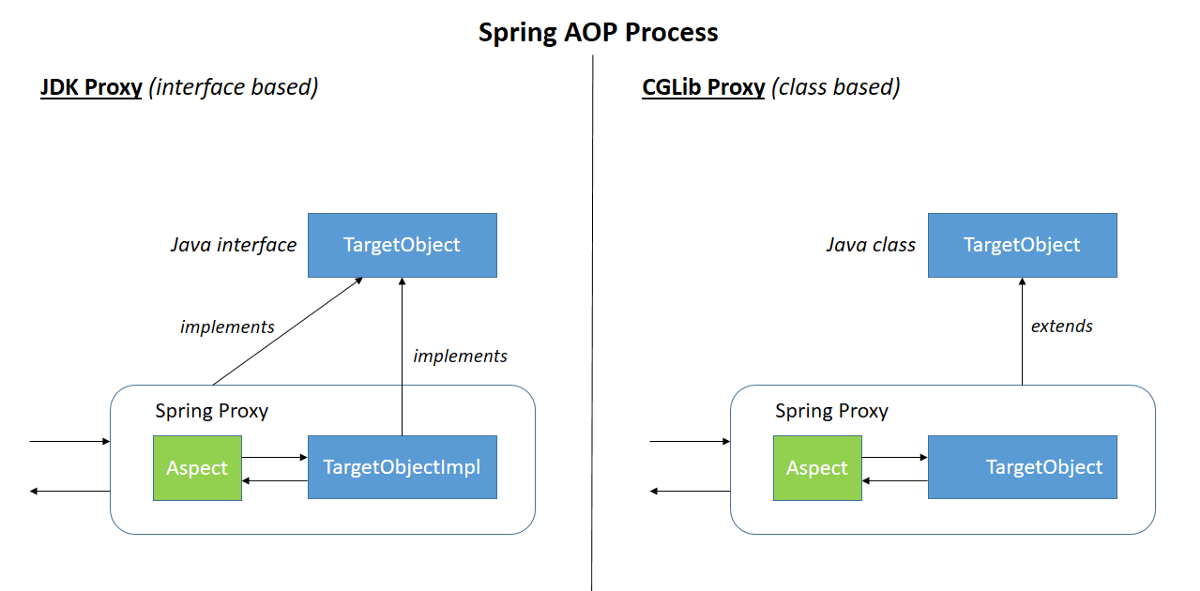
우선 @Transactional 어노테이션은 AOP 기능을 기반으로 동작을 합니다. Spring에서 AOP는 두가지 방법으로 구현을 합니다.
AOP에 대한 자세한 내용은 해당 포스트에 좋은 글이 있어 공유 합니다. ( https://steady-coding.tistory.com/608 )
AOP란?
AOP는 이러한 교차 관심사를 분리하여 별도의 모듈로 만들고, 이를 필요한 시점에 적용하도록 합니다. 이렇게 함으로써 기능별로 코드를 분리하고 재사용성을 높이며, 유지 보수성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming)는 교차 관심사(cross-cutting concerns)를 모듈화하는 프로그래밍 패러다임입니다. 교차 관심사는 여러 클래스나 메서드에서 공통으로 적용되는 기능을 말합니다. 예를 들어, 로깅, 보안, 트랜잭션 관리 등이 이에 해당합니다.
- 다이나믹 프록시 방식
- 특징인터페이스를 기반으로 프록시 객체를 생성한다
- 리플렉션을 통해서 프록시 객체를 만든다.
- CGLIB 방식
- 특징타겟의 클래스를 상속받아 프록시를 생성한다.
- 클래스의 바이트 코드를 조작하여 프록시 객체를 만든다.
@Transactional 어노테이션을 사용할 때 기본으로는 CGLIB를 기반으로 작동합니다.
// 기본 값은 true 입니다.
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnBean(TransactionManager.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class)
public static class EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false",
matchIfMissing = false)
public static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true)
public static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
설정 파일을 바꾸어서 JdkDynamicAopProxy를 사용할 수 있습니다
// appication.yml
spring:
aop:
proxy-target-class: false
CglibAopProxy에서 TransactionIntercepter 를 호출하고 invoke 명령어를 통해서 TransactionAspectSupport을 호출합니다.
// TransactionIntercepter.java
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
// The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
// as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
// Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport's invokeWithinTransaction...
return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new CoroutinesInvocationCallback() {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object getTarget() {
return invocation.getThis();
}
@Override
public Object[] getArguments() {
return invocation.getArguments();
}
});
}
그렇다면 TransactionAspectSupport은 어떻게 동작하는 지 살펴 봅시다
@Nullable
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
// transaction 정보를 가져온다
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final TransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
// Reactive Transaction Manager 처리
if (this.reactiveAdapterRegistry != null && tm instanceof ReactiveTransactionManager rtm) {
....
}
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
// Standard Transaction Manager 처리
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager cpptm)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
...
}
// Callback Preferring Transaction Manager 처리
else {
Object result;
final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
// It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
....
}
메서드는 주로 세 부분으로 나눌 수 있으며, 각각 다른 유형의 트랜잭션 매니저를 처리하는 방법에 대해 설명하고 있습니다.
- Reactive Transaction Manager: 이 부분은 ReactiveTransactionManager를 처리합니다. 반응형 프로그래밍을 위해 사용되는 트랜잭션 매니저입니다. 코루틴이 지원되는지 체크하고, 코루틴 함수의 경우에 대한 별도 처리를 합니다. 트랜잭션 내에서 메서드를 호출하고 결과를 반환합니다.
- Standard Transaction Manager: 이 부분은 일반적인 PlatformTransactionManager를 처리합니다. 트랜잭션을 시작하고, 메서드를 호출한 뒤, 에러가 발생하면 롤백하고, 아니면 커밋합니다. Vavr 라이브러리를 사용하는 경우에 대한 추가 처리를 합니다.
- Callback Preferring Transaction Manager: 이 부분은 CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager를 처리합니다. 트랜잭션을 시작하고, 메서드를 호출한 뒤, 결과를 반환합니다. 트랜잭션 내에서 예외가 발생하면 롤백하고, 아니면 커밋합니다.
저희는 Standard Transaction Manager를 사용하므로 Standard Transaction Manager를 좀 더 자세히 살펴 보겠습니다.
PlatformTransactionManager ptm = asPlatformTransactionManager(tm);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(ptm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager cpptm)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 트랜잭션이 시작되지 않았다면 Transaction 설정을 기반으로 Transaction을 시작합니다.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(ptm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 로직 실행
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
// transaction 이후에 exception이 있는 경우 transaction 처리
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 함수형 인터페이스 체크
if (retVal != null && vavrPresent && VavrDelegate.isVavrTry(retVal)) {
// Set rollback-only in case of Vavr failure matching our rollback rules...
TransactionStatus status = txInfo.getTransactionStatus();
if (status != null && txAttr != null) {
retVal = VavrDelegate.evaluateTryFailure(retVal, txAttr, status);
}
}
// commit 처리
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
- 처음에는 tm이라는 TransactionManager를 PlatformTransactionManager로 변환합니다.
- 트랜잭션이 시작되지 않았다면 Transaction 설정을 기반으로 Transaction을 시작합니다.
- 그리고나서 실제 비즈니스 로직을 실행합니다. 만약 로직 실행 중에 오류가 발생하면, 트랜잭션을 롤백하거나 커밋하고 오류를 처리합니다. 로직 실행이 끝나면 트랜잭션 정보를 정리합니다.
- 이 과정에서, 만약 Vavr라는 라이브러리를 사용하여 함수형 프로그래밍이 이루어졌다면, 실패한 경우에 트랜잭션 상태를 변경할 수 있도록 추가적인 처리를 합니다.
- 마지막으로, 비즈니스 로직의 실행이 성공적으로 끝나면 트랜잭션을 커밋합니다. 만약 이 과정에서 오류가 발생하면 적절하게 처리합니다.
- 마지막으로 비즈니스 로직의 결과를 반환합니다.
그렇다면 rollback 처리는 어떻게 이루어지는 지 확인합니다. rollback 처리는 completeTransactionAfterThrowing에서 처리를 합니다.
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
실제로 존재하고 아직 완료되었는지 확인을 위해, 먼저 txInfo와 txInfo의 TransactionStatus가 null이 아닌지 확인합니다.
이후 txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)가 true를 반환하면, 즉 현재 예외가 롤백을 유발해야 하는 경우, 트랜잭션을 롤백합니다. 만약 false를 반환한다면, 트랜잭션을 커밋합니다.
그렇다면 txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex) 는 어떻게 판별하는 지 알아봅시다.
기본으로는 DefaultTransactionAttribute의 rollbackOn을 사용합니다. 코드는 다음과 같습니다
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);
}
ex이 Error와 RuntimeException에 대해서 true를 return 하고 있습니다
결론
- @Transactional 은 AOP 기반으로 동작하며 default는 CGLIB이다
- @Transactional은 일반적으로 PlatformTransactionManager 을 사용한다.
- rollback의 경우는 Error | RuntimeException 이 반환되었을 때 한다
https://techblog.woowahan.com/2606/
https://private-space.tistory.com/98
https://steady-coding.tistory.com/608
https://sup2is.github.io/2021/03/04/java-exceptions-and-spring-transactional.html